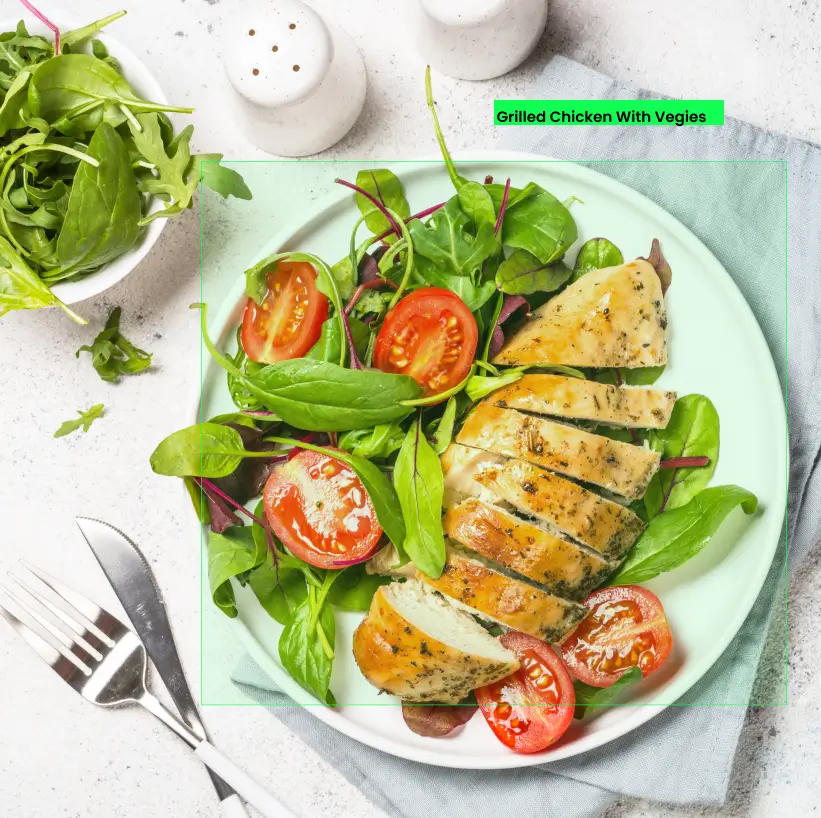
AI Powered Food Recognition API
Folio3 AI’s Food Recognition API is a cutting-edge, AI-powered platform designed to accurately identify food items in images. Leveraging advanced computer vision and artificial intelligence, our API can detect, recognize, and even classify various food items with ease.
Advanced Deep Learning Based Food Recognition APP
With our AI powered food recognition API perform tasks from identifying fruits, vegetables, and ingredients to powering innovative solutions in health, retail, and beyond—our API is your gateway to the future of food recognition.

Food Identifier Solution Features
Our solution based on our pre-built model helps you crunch through your data sets with ease and dig up key insights in terms of food type, food groups, dish recognition, etc.

High Accuracy Recognition
Our API utilizes advanced AI algorithms to achieve high accuracy in identifying a wide variety of food items in images and vide feeds, even in challenging conditions such as poor lighting, partial obstructions, or unconventional angles.

Real-Time Processing
Experience real-time food detection with rapid processing speeds, enabling immediate identification and seamless integration into time-sensitive applications like retail checkouts or live culinary demonstrations.
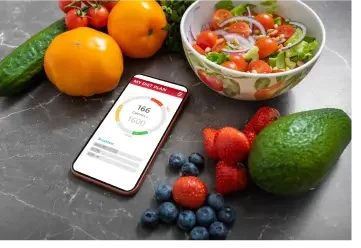
Produce Nutritional Information
Automatically generate detailed nutritional information for identified food items, including calorie count, macronutrient breakdown, vitamins, and minerals. This feature is perfect for health and wellness applications, dietary planning, and nutritional analysis.

Recognition and Classification of Various Food Items
The Food API ensures comprehensive recognition and classifcation capabilities that cover everything from common fruits and vegetables to exotic ingredients and prepared dishes.

Customizable Detection Parameters
Tailor the detection settings to your specific needs. Whether you need to focus on certain categories of food or adjust sensitivity levels, the API offers customizable parameters to optimize performance for your unique use case.

Seamless API Integration
Folio3 AI's Food Recognition API is designed for easy integration with existing systems. Whether you're working on a mobile app, a web platform, or a point-of-sale system, our API can be seamlessly embedded to enhance functionality without disrupting your existing workflows.

Scalable Infrastructure
Built on a robust and scalable infrastructure, the API can handle varying loads, from small-scale applications to large enterprise deployments, ensuring consistent performance as your usage grows.
Use Our Food Recognition API for Different Industry Verticals
Folio3 AI’s Food Recognition API offers advanced visual analysis capabilities, unlocking opportunities across various industries.

Health and Wellness Apps
Integrate with health and wellness applications to help users track dietary choices, monitor calorie intake, and maintain a balanced lifestyle.
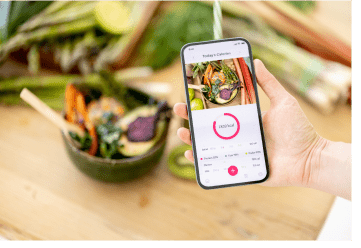
Cooking Tools and Recipe Apps
Enhance cooking tools and recipe apps with automatic food item recognition.

Produce Sorting and Quality Control
Automate sorting and quality control processes in the food industry.

Retail Solutions and Self-Checkout Counters
Streamline checkout processes and minimize fraud in retail environments.

Food Waste Reduction
Implement solutions to identify and reduce food waste.
Custom Development and Innovation
Customize the API to develop innovative applications tailored to your business needs.

Culinary Education and Nutritional Analysis
Use the API for educational tools and nutritional analysis in culinary schools and beyond.

Automated Inventory Management
Simplify inventory management with automated food recognition.

Menu Planning and Personalized Recommendations
Leverage AI for menu planning and personalized food recommendations.

Food Safety Compliance
Ensure compliance with food safety standards through accurate food identification.
Benefits of Folio3 AI Food Recognition API
Enhanced User Experience
Integrate our API to provide users with a seamless and intuitive experience by automatically identifying food items within your applications.
Versatility and Flexibility
Whether in health and wellness, culinary tools, or retail, the Food Recognition API is versatile, catering to a wide range of industries and usage scenarios.

Improved Quality Control
Ensure the accuracy and consistency of food identification in quality control applications, guaranteeing that only the finest products reach your customers.

Efficient Retail Solutions
Utilize the API in retail settings, such as self-checkout counters, to streamline checkout processes, minimize fraud, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Custom Development
Tailor the API to your specific needs, unlocking endless possibilities for unique projects and groundbreaking solutions.

Automated Produce Sorting
Automate produce sorting processes using our API, saving time and boosting efficiency within food supply chains.
Cost-Effective Solution
Reduce manual labor costs and enhance operational efficiency with automated food recognition.
Cutting-Edge Technology
Harness the power of visual analysis and AI to stay ahead in the rapidly evolving field of food recognition.
Streamline Your Project with Our Step-by-Step Approach
1

Identify the problem
2

Define success criteria
3

Determine the solution
4

Collect training data
5

Train & Evaluate
6

Deploy and test
7

Iterate on the solution
Food Detection
Solutions
Learn more about the solution
And standard features.
Why Choose Folio3 AI’s Food Recognition API?

20+ Pre-built Models Deployed
We have worked on multiple projects deploying more than 20 pre-built AI models on various global projects.

15+ Years of Experience
We have developed purpose-built AI solutions that help maximize performance based on more than 15 years of experience. We have worked in various scenarios that help us identify your problem quickly and develop insightful.

1000+ Enterprise-Level Clients
Over the last 15 years, we've built an extensive client base of delighted customers!
Computer Vision Excellence
With years of experience in AI and computer vision technologies, Folio3 brings unparalleled expertise to the field of workplace safety management.
Scalability and Flexibility
We offer scalable and flexible AI models that are easy to integrate into existing infrastructure.
Food Detection Solution FAQs
How does food detection work?
The food detection system is based on computer vision technology to identify and detect the presence of any foreign object in packaged foods.




