Precision medicine is diligently redefining healthcare personalized treatment. It shifts from a one-size-fits-all approach to providing customized checkups due to variations in individual genetics, lifestyle, and environment. However, AI is mandatory for precision medicine, as it addresses this problem by analyzing massive amounts of data, including genomics, medical history, and lifestyle factors, to develop tailored treatment strategies.
AI for precision medicine uses machine learning algorithms to predict the most effective treatments for specific patient needs. It also leads to improved outcomes and mitigates healthcare costs. In this guide, you will see how AI holds the promise of supporting timely decision-making and intervention in acute care, as well as its applications, benefits, challenges, and steps to implementation.
What is AI in Precision Medicine?
Precision medicine leverages detailed information about a patient’s genetic makeup, environment, and lifestyle to deliver highly personalized care. AI amplifies this approach by analyzing vast amounts of data, identifying patterns, and offering actionable insights faster than ever before. Modern AI systems such as Google’s DeepMind and IBM Watson showcase how advanced algorithms assist in deciphering complex medical data. These technologies go beyond simple analytics, simulating predictive models for diseases and analyzing genomic information to deliver tailored treatment plans.
Dr. Eric Topol, Cardiologist and Author of Deep Medicine:
“AI is the most important tool we have to individualize care for patients. It will allow us to deliver precision medicine on a large scale.”
For a better understanding, check out this video for insights on AI’s transformative role in precision medicine.
AI Role in Revolutionizing Healthcare
AI bridges the gap between generalized care and individualized solutions, bringing us closer to truly patient-centric healthcare. Studies reveal that AI-powered platforms have trimmed the drug discovery timeline by as much as 50%, slashing costs and accelerating the journey from lab to market. AI doesn’t just analyze; it learns and adapts. Its role in healthcare includes.
- Creating personalized disease risk profiles.
- Supporting real-time patient monitoring.
- Speeding up the drug development process.
Why AI is Key for Precision Medicine
AI has become indispensable in precision medicine due to its unparalleled ability to are:
- Process large datasets efficiently, such as genomic sequences, electronic health records (EHRs), and sensor data from wearables.
- Identify subtle patterns and correlations invisible to traditional analysis methods.
- Improve predictive accuracy for disease risks, treatment outcomes, and recovery trajectories.
- Predictive models that are powered by AI can transform chronic disease management by providing early warnings for conditions like diabetes, cancer, and cardiovascular diseases.
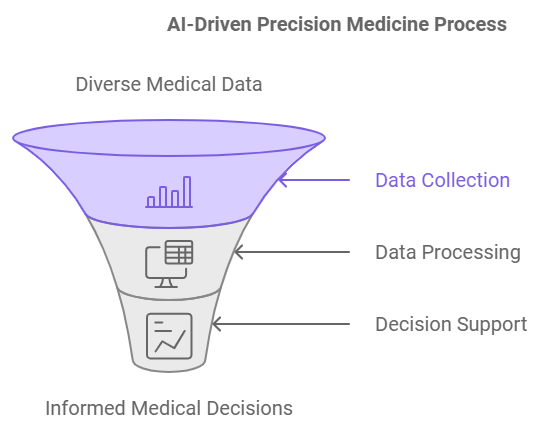
How AI Works in Precision Medicine
AI technologies such as machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing(NLP) are the backbone of precision medicine. These tools excel at extracting insights from raw data to drive informed medical decisions. Down below are detailed steps on how it works.
1. Data Collection
AI gathers data from diverse sources:
- Genomic sequencing: Analyses DNA to identify mutations linked to diseases.
- Electronic health records (EHRs): Aggregates a patient’s medical history for holistic analysis.
- Wearable devices: Tracks vital signs and physical activity continuously.
- Medical imaging: Interprets X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans to identify anomalies.
2. Data Processing and Analysis
After data collection, AI algorithms:
- Identify genetic markers and trends associated with specific conditions.
- Analyse imaging results to detect early signs of diseases.
- Combine environmental and lifestyle factors** with genetic data for a comprehensive health profile.
3. Decision Support
AI systems support clinicians in making better decisions by:
- Predicting potential disease risks.
- Recommending evidence-based, personalized treatment options.
- Suggesting preventive measures tailored to individual patients.
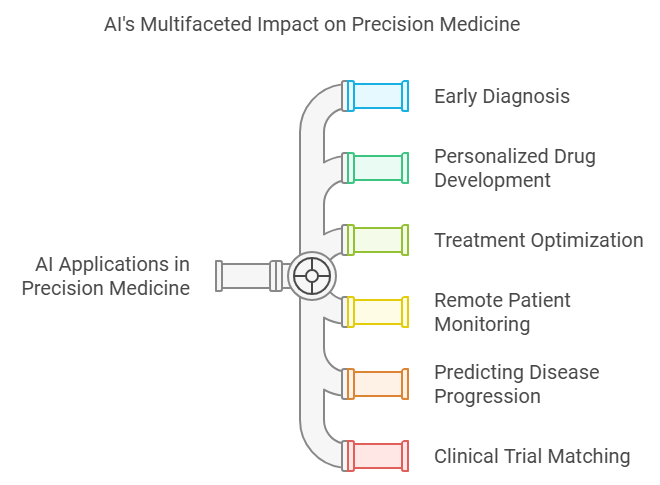
Key Applications of AI in Precision Medicine
AI’s role in cancer diagnosis is transformative, achieving accuracy that often exceeds human pathologists. It enhances early detection, reduces missed diagnoses, and predicts metastasis, but biases in data must be addressed for equitable healthcare. These are discussed below.
- Early Diagnosis: AI excels at identifying early warning signs, sometimes years before symptoms appear.
- Personalized Drug Development: AI has accelerated drug discovery by simulating chemical reactions and analyzing biological pathways.
- Treatment Optimisation: AI tailors treatment plans by analyzing a patient’s genetic profile, lifestyle, and medical history.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Wearable devices and Internet of Things (IoT) sensors collect real-time data that AI analyses to ensure proactive care.
- Predicting Disease Progression: AI models analyze patient data to predict how a disease will progress, allowing for earlier interventions and more effective treatment plans.
- Clinical Trial Matching: AI algorithms can match patients with appropriate clinical trials by analyzing their genetic and medical profiles, ensuring they receive access to the latest therapies.
- Optimizing Resource Allocation: AI helps healthcare systems efficiently allocate resources, such as ICU beds and medical staff, by predicting patient needs and disease trends, improving care delivery, and reducing costs.
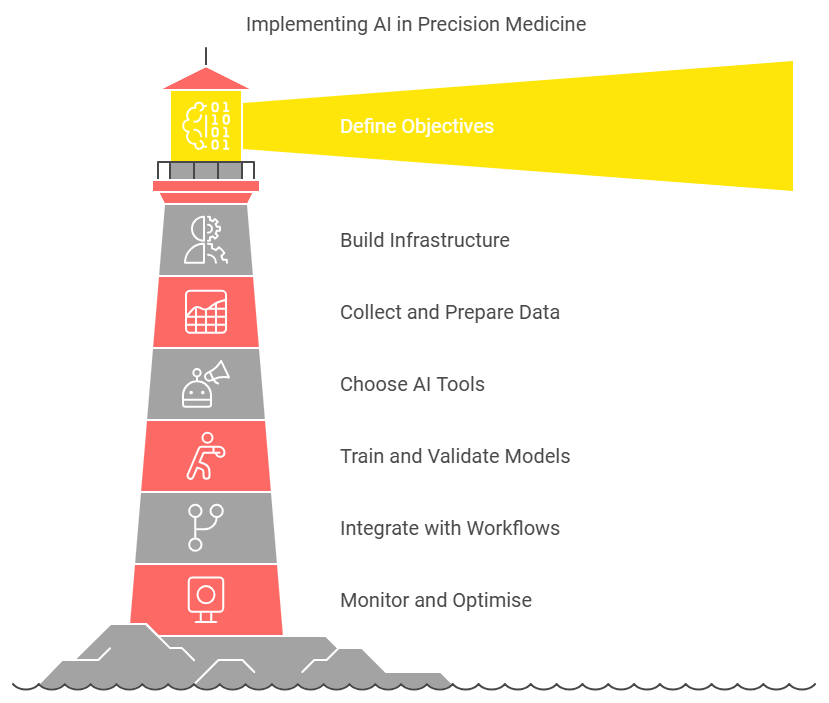
Steps to Implement AI in Precision Medicine
AI can improve decision-making in treatment selection and dosing, particularly in complex cases involving combination therapies. It also upgrades data accuracy and supports personalized medicine by optimizing patient care, drug discovery, and clinical trials. However, it also faces challenges such as data quality, privacy concerns, algorithm biases, and high implementation costs. Therefore below are the steps to implement AI in precision medicine that potentially improve diagnostic accuracy, treatment outcomes, and healthcare efficiency.
Here’s a more concise version with a bit more detail:
Step 1. Define Objectives
Clarify whether you aim to improve diagnostics, enhance treatment precision, optimize drug development, or enable proactive preventive care.
Step 2. Build Infrastructure
Develop the necessary data pipelines, computing infrastructure, and AI tools to handle and process large datasets efficiently at scale.
Step 3. Collect and Prepare Data
Gather diverse, high-quality datasets from various sources, ensuring that data is clean, structured, and suitable for training AI models.
Step 4. Choose the Right AI Tools
Select suitable AI technologies like Natural Language Processing for extracting data insights and Machine Learning for making predictive analytics.
Step 5. Train and Validate Models
Test AI models thoroughly for accuracy, reliability, and bias, ensuring that they perform consistently before clinical deployment.
Step 6. Integrate with Clinical Workflows
Seamlessly integrate AI into clinical workflows, providing clinicians with user-friendly interfaces and comprehensive training for smooth adoption.
Step 7. Monitor and Optimise
Constantly monitor system performance and optimize models based on new data, technological advances, and feedback from healthcare providers.
Future Trends in AI and Precision Medicine
Precision medicine tailors healthcare to an individual’s unique genetic makeup and health data, enabling personalized treatment and earlier disease detection. Advances like electronic health records (EHRs) and genetic testing are enhancing diagnoses and improving care by focusing on individual characteristics rather than general patient trends.
- AI-Driven Genomic Editing: Advanced algorithms combined with CRISPR technology will redefine genetic disease treatment.
- Edge AI in Wearables: Real-time, on-device processing will enable accurate and instant health insights.
- Collaborative Platforms: Global data-sharing platforms will facilitate breakthroughs in personalized medicine.
- AR/VR Integration: Augmented and virtual reality tools will improve surgical precision and patient education.
- AI-Driven Drug Repurposing: AI algorithms can analyze existing drugs’ effects on different diseases, speeding up the process of identifying new treatments for various conditions.
- Predictive Analytics: AI models will enable early risk assessments for diseases like diabetes and Alzheimer’s, predicting potential outcomes based on genetic and lifestyle factors.
- Virtual Health Assistants: These assistants will continuously provide real-time health advice and monitor patients’ conditions, offering personalized guidance and medical alerts.
Conclusion: Transforming Healthcare for the Better
AI is changing how we approach precision medicine, helping doctors provide more personalized and proactive care. It enables early detection of diseases, improves treatment plans, and speeds up the discovery of new drugs. AI tools such as empathetic chatbots facilitate patient engagement and improve the overall care experience. While challenges persist, the potential for AI to revolutionize healthcare is immense, promising better outcomes and a more equitable system for all patients.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
It contributes by analyzing vast amounts of medical data, identifying disease patterns and risk factors, and designing treatment plans according to individual genetic profiles.
The benefits of having AI for precision medicine are the earlier detection of diseases, more efficient clinical trials, and accelerated drug discovery.
Some ethical concerns exist, such as data privacy, access fairness, and algorithms’ potential biases. However, it has been taken care of through regulations and guidelines to ensure AI’s transparent and ethical use in healthcare.
It recognizes patient data to create tailored treatment plans considering genetics, lifestyle, and medical history, optimizing therapeutic outcomes.
Some real-world examples are IBM Watson Health, which assists oncologists in treatment decisions; Google DeepMind, which predicts acute kidney injury; and KenSci, which predicts patient readmissions.
AI algorithms consider a patient’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and medical history to recommend treatments that are most likely to be effective, reducing the trial-and-error approach often seen in mental health care.

Manahil Samuel holds a Bachelor’s in Computer Science and has worked on artificial intelligence and computer vision She skillfully combines her technical expertise with digital marketing strategies, utilizing AI-driven insights for precise and impactful content. Her work embodies a distinctive fusion of technology and storytelling, exemplifying her keen grasp of contemporary AI market standards.