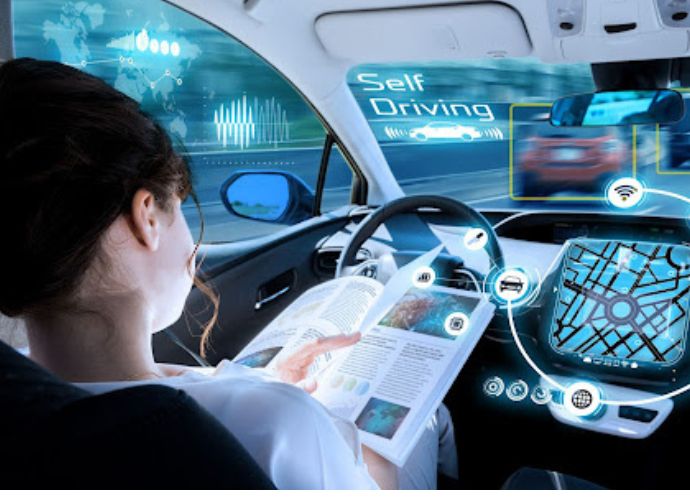
The global automotive AI market is on track for substantial growth in the coming years, driven by rapid technological advancements and increasing adoption across the industry.
From AI in automotive manufacturing and smart in-vehicle systems to optimizing logistics and predicting maintenance, artificial intelligence in vehicles is reshaping how we design, build, and drive cars.
No longer limited to factory robots, AI now powers predictive analytics, generative design, and self-learning systems.
Inside vehicles, it supports real-time decision-making, driver assistance, and personalized experiences.
This article explores the evolution, applications, and real-world impact of AI across the automotive industry—covering production, mobility, safety, and user satisfaction.
The Evolution of AI in Automotive
AI has come a long way in the automotive world—from early automation and electronics to the complex intelligence powering autonomous vehicles today.
Its evolution has transformed everything from factory floors to in-car experiences.
Autonomous Driving
Self-driving technology depends heavily on AI to function effectively and safely.
- Levels of Autonomy:
Driving automation ranges from Level 1 to Level 5.
- Level 1: Driver assistance, like cruise control or lane keeping—driver remains fully engaged.
- Level 2: Partial automation—car can control steering and speed, but the driver must monitor and intervene anytime.
- Level 3: Conditional automation—car handles driving in specific conditions; the driver must be ready to take over when prompted.
- Level 4: High automation—vehicle drives itself in defined environments (e.g., urban shuttles); no driver needed within those zones.
- Level 5: Full automation—no human input required at any time; no steering wheel or pedals needed.
Most current vehicles are classified as Level 2 or Level 3, which means they offer features like adaptive cruise control, lane centering, and some degree of hands-free driving under certain conditions.
- Sensor Fusion: AI processes real-time data from various inputs like cameras, LiDAR, radar, and ultrasonic sensors to interpret the environment around the vehicle and make informed decisions.
- Navigation & Obstacle Detection: AI systems in vehicles such as Tesla Autopilot and Waymo analyze road changes, predict possible obstacles, and adjust routes to avoid collisions and improve travel efficiency.
Predictive Maintenance
AI in car manufacturing has enabled real-time diagnostics and proactive maintenance.
- Early Detection: Using sensors and machine learning algorithms, AI continuously monitors engine health, battery performance, brake systems, and other components to catch potential issues before they escalate.
- Outcome: This predictive capability reduces unexpected breakdowns and improves vehicle longevity—highlighting one of the major benefits of AI in automotive industry maintenance practices.
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
ADAS leverages artificial intelligence in automobiles to enhance driving safety and awareness.
- It has features such as lane-keeping assist, blind spot alerts, forward collision warnings, and adaptive cruise control that are now standard in many new vehicles.
- AI’s Role: These systems rely on AI to process input from the vehicle’s sensors and cameras, allowing for timely and accurate reactions to sudden road hazards and changes in traffic flow.
Smart Manufacturing and Robotics
AI in automotive manufacturing has redefined how vehicles are produced.
- Repetitive Tasks: AI-powered robots perform high-precision tasks like welding, painting, and assembly, improving consistency and reducing errors on production lines.
- Generative Design and Digital Twins: These AI tools simulate vehicle performance, optimize parts before production, and help engineers test concepts virtually, saving time and resources.
In-Vehicle Personalization and Assistance
Artificial intelligence in vehicles enhances the driver’s experience through customization and automation.
- Voice Commands and Customization: In-car assistants, like Amazon Alexa Auto or BMW’s Intelligent Personal Assistant, respond to natural speech, adjust climate settings, suggest routes, and play personalized media content.
- Route Optimization: AI uses traffic patterns, weather data, and driver history to suggest the fastest, safest, and most efficient driving routes in real time.
Supply Chain and Inventory Optimization
The impact of AI in automotive industry logistics is often overlooked but highly valuable.
- Inventory Monitoring: AI tracks raw materials and parts through every stage of the supply chain, ensuring timely procurement and preventing stockouts.
- Demand Planning: Predictive models assess historical data and market trends to forecast demand, helping manufacturers avoid overproduction and minimize delays.
Benefits of AI in the Automotive Industry
The benefits of AI in automotive industry operations are broad and impactful.
Increased Safety and Fewer Accidents:
AI systems enhance vehicle safety through lane-keeping, collision warnings, adaptive cruise control, and obstacle detection, significantly reducing the risk of accidents and supporting safer driving in real-time conditions.
Lower Operational and Maintenance Costs:
Predictive maintenance powered by AI identifies potential issues before failures occur. This reduces downtime, prevents costly repairs, and helps operators manage maintenance schedules efficiently, saving both time and money.
Improved Customer Satisfaction and Personalization
AI tailors in-vehicle experiences by learning driver preferences. From seat position to infotainment and navigation, it creates a more responsive, enjoyable, and personalized journey for every individual.
Enhanced Efficiency in Manufacturing and Logistics
AI optimizes factory workflows using robotics, digital twins, and predictive analytics. It streamlines supply chains, reduces material waste, and improves delivery precision for faster, more cost-effective production cycles.
Support for Connected and Smart Mobility Ecosystems:
AI enables vehicles to interact with infrastructure and other cars. This connectivity enhances traffic flow, supports smart city development, and lays the groundwork for future autonomous and shared mobility systems.
Enhanced Cybersecurity:
AI systems monitor for unusual activity, detect intrusions, and respond in real time. This protects onboard software, driver data, and connectivity features from evolving cyber threats and unauthorized access.
Improved Vehicle Performance and Longevity:
AI helps maintain optimal engine performance by analyzing driving patterns, calibrating systems, and ensuring timely maintenance. This improves energy efficiency and extends the vehicle’s operational lifespan over time.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Here’s how global automakers are leveraging artificial intelligence in automobiles and beyond:
Case Study 1: Tesla’s Autopilot AI System
Tesla recorded one crash for every 7.44 million miles driven using Autopilot technology, compared to one crash for every 1.51 million miles without Autopilot and approximately 702,000 miles for the U.S. average Tesla Vehicle Safety Report | Tesla.
The system leverages massive real-world driving data from over 9 billion miles to continuously improve autonomous driving capabilities and enhance vehicle safety through AI-powered predictions and real-time decision making.
Case Study 2: BMW’s AI Manufacturing Quality Control
BMW’s Regensburg plant achieved the world’s first end-to-end digitalised and automated process to inspect, process and mark painted vehicle surfaces in series production, where AI-controlled robots apply objective quality standards to process each vehicle individually Automated Surface Processing.
This innovative system eliminates human error in quality inspection, reduces production defects, and enables real-time manufacturing adjustments for improved efficiency.
How Is the Automotive Industry Impacting the US with AI Adoption?
AI is rapidly transforming the U.S. automotive industry, driving innovation in vehicle technology, manufacturing, and customer experience. Here’s how AI is shaping the future of mobility across America:
1. Autonomous Driving
AI powers self-driving systems, enabling vehicles to make real-time decisions using data from sensors and cameras, significantly improving safety and reducing reliance on human drivers.
2. Predictive Maintenance
Machine learning detects potential issues before they happen, helping drivers and fleet operators avoid costly repairs and downtime through intelligent maintenance alerts and diagnostics.
3. Smarter Manufacturing
AI enhances production lines with robotics, quality control, and supply chain optimization, allowing automakers to produce vehicles more efficiently and reduce manufacturing errors.
4. Personalized Driver Experience
AI systems customize in-car settings like navigation, music, and climate control, offering drivers a seamless, intuitive experience tailored to their preferences.
5. Traffic and Infrastructure Optimization
AI helps cities manage traffic flow through smart signals and V2X technologies, reducing congestion and emissions while improving overall transportation efficiency.
Regulations and Global Perspectives
The development and deployment of AI in the automotive industry are influenced by evolving global regulations:
- United States: The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) provides guidelines for testing and deploying AI-driven driving systems, focusing on innovation without compromising safety.
- European Union: The EU AI Act classifies autonomous vehicles as high-risk AI systems and mandates strict safety and transparency standards to ensure public trust and accountability.
- China: Government-backed initiatives like Baidu Apollo benefit from a supportive regulatory environment that encourages smart city testing and rapid AI integration.
- India: India is investing in AI-powered traffic management, predictive maintenance for public vehicles, and telematics, with mobility startups like Ati Motors leading the innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions
As AI in the automotive industry becomes more mainstream, many people have questions about its capabilities and implications.
What’s the difference between ADAS and autonomous driving?
ADAS supports human drivers with features like cruise control and lane assist, while autonomous driving goes further, allowing vehicles to control themselves in specific conditions with minimal or no human input.
Can AI fully replace human drivers?
Not yet. While AI has advanced considerably, fully autonomous systems still struggle in unpredictable environments. Legal, ethical, and technical challenges must be addressed before human drivers can be entirely replaced.
How does AI affect insurance?
AI helps insurers analyze vehicle usage data, predict risks more accurately, personalize coverage, and process claims faster using automated decision-making systems.
Where is AI used in automotive?
AI is used in nearly every phase of the automotive process—from design and manufacturing to navigation, diagnostics, logistics, and even in-cabin personalization features.
Final Thoughts
The automotive industry is no longer just a futuristic concept—it’s already redefining mobility.
From AI in car manufacturing to intelligent driving systems, its integration is delivering tangible improvements in safety, efficiency, personalization, and sustainability.
As the impact of artificial intelligence in automotive industry practices continues to grow, the road ahead looks smarter, safer, and more connected than ever.
Automakers who embrace these technologies are not only future-proofing their businesses but also helping to shape the next era of intelligent transportation.

Laraib Malik is a passionate content writer specializing in AI, machine learning, and technology sectors. She creates authoritative, entity-based content for various websites, helping businesses develop E-E-A-T compliant materials with AEO and GEO optimization that meet industry standards and achieve maximum visibility across traditional and AI-powered search platforms.