Executive Summary:
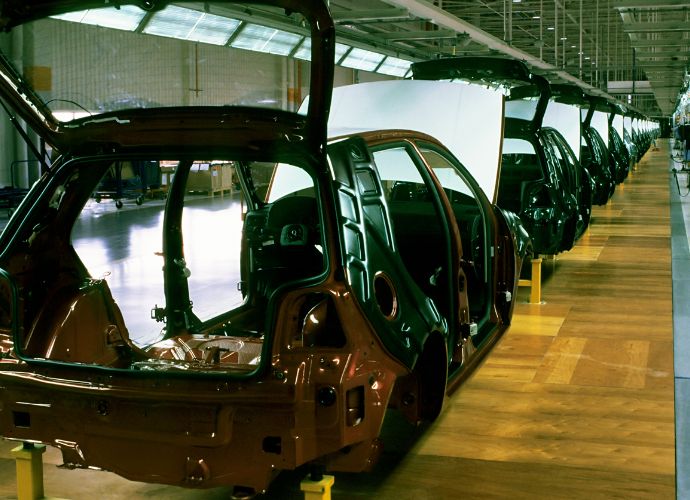
Many industries have been impacted by artificial intelligence (AI), but the manufacturing and automotive sectors have seen the most significant influence. According to projections, the automobile industry’s use of AI will expand at a compound annual growth rate of about 40% to $15.9 billion by 2027. In addition, the demand for intelligent technologies like speech and image recognition and connected cars is rising steadily around the globe. As a result, autos’ design, manufacture, and use will continue to rely on automation and AI.
What Influence Is AI Having on the Automotive Sector?
The automobile sector has used automation for many years, but AI has changed that. Moreover, because ML and AI can foresee the future, they have a much greater capacity to change the automotive industry than we have seen in the past.
Because of the emergence of Industry 4.0, AI’s influence is no longer limited to aiding in creating self-driving cars. It has instead spread to produce much more significant and profound outcomes. The automotive industry is looking to use AI and ML to boost development cycles, cut costs, enhance efficiency, optimize products, and build a more sustainable ecosystem. We can clearly understand its impact when we state that it is no longer discretionary for automobile makers to imbibe it. They must do this in order to survive.
Here are three ways AI impacts the automobile industry and why people need to be upskilled.
- Road Conditions Analysis
Every year, over 1000 individuals in the US are killed needlessly by cars that run red lights. The transportation structure cannot be questioned, yet human nature frequently causes havoc. This issue might be resolved by developing intelligent cities and AI-powered automobiles.
Vehicles can now monitor road conditions autonomously thanks to AI-based technology. For instance, the software can identify traffic signals by automated imaging, and if it determines that the color is red, it will immediately apply the brakes. To further enhance user experience, the system also uses additional elements like traffic flow analysis and pedestrian mapping.
- Usage of Big Data
For a while now, big data has been a popular term across many businesses, and for a good reason. Data sets with greater diversity, more incredible velocity, and greater volume than ever before are referred to by this word. But unfortunately, these data sets are too big and complicated to be processed using conventional methods; instead, sophisticated statistical frameworks and intricate algorithms are needed.
Data on consumer behavior and preferences, driving habits, geographic locations, and other information are all examples of big data in the automotive sector. Furthermore, big data is a critical component of many artificial intelligence applications, emphasizing the importance of data analytics knowledge for automotive engineers.
- Logistics for Supply Chain Management
With an average passenger automobile having over 30,000 parts, there are several potentials for supply chain hiccups to result in significant manufacturing delays. Automobile firms can use advanced supply chain analytics to foresee supply problems caused by everything from local weather occurrences to geopolitical shocks like COVID-19. As a result, automotive manufacturers can plan for disruptions while keeping a lean and efficient operation with enhanced visibility into areas of concern.
- Producing the Cars That Customers Want
Future automobiles can be designed by automakers using big data analytics to consider shifting consumer tastes and needs. Manufacturers can identify features in demand and determine what price point would make them economically viable for the customer using data from customer interactions to social media discussions. Extensive data analysis is used, for instance, by Hyundai to generate “customer-centric services or products.” In addition, businesses can use big data to track rivals’ products and use the knowledge to inspire new items in the future.
- Creating Marketing Campaigns with a Specific Audience
Big data in the automotive sector is quite beneficial when selling cars to customers. Automobile manufacturers can use data analytics to examine their current clientele and uncover traits that indicate a likelihood of buying. In addition, big data can assist automakers in personalizing marketing messaging and disseminating pertinent material by providing information about past vehicle purchases, online behavior, and demographics. Even better, they can utilize it to pinpoint dealership sites that will enhance client retention.
- Autonomous vehicles
According to PwC research, driverless vehicles could account for 40% of all miles driven in Europe by 2030. Although numerous automakers, including Tesla, Ford, and others, have tested and integrated autonomous vehicle detection industry capabilities into their vehicles, the current results could be more impressive. However, we still need to conclude that fully autonomous cars will become a reality within the next few years.
Although the technology would need to be tested, the idea of a semi-driverless vehicle detection industry has already been floated. Examples of partially autonomous automobiles include Tesla’s Autopilot and several other brands that offer self-parking and lane assistance.
Conclusion:
Without a doubt, we are only beginning to explore the full potential of AI in all sectors. Data Science, Machine Learning, Artificial Neural Networks, and Text Mining are all technologies with a lot to offer manufacturing in general and the automobile industry in particular. In addition, these technologies are already mature in online marketing and finance.
The whole lifetime of a vehicle, from design and development to testing, manufacture, and marketing, can benefit from using artificial intelligence (AI).
Powerful sources of information include the data collected by the numerous sensors that are now integrated into the vehicle detection industry, taken from production lines, and collated from consumer feedback. Equally powerful levers for design, testing, and maintenance improvement, as well as for comprehending user needs and expectations, are provided by their analysis and interpretation. Looking further into the future, the issue is undoubtedly the development of the autonomous vehicle detection industry and the entire delegation of all safety-related choices to the vehicle itself. This challenge is both challenging and inspiring.

Dawood is a digital marketing pro and AI/ML enthusiast. His blogs on Folio3 AI are a blend of marketing and tech brilliance. Dawood’s knack for making AI engaging for users sets his content apart, offering a unique and insightful take on the dynamic intersection of marketing and cutting-edge technology.