Introduction
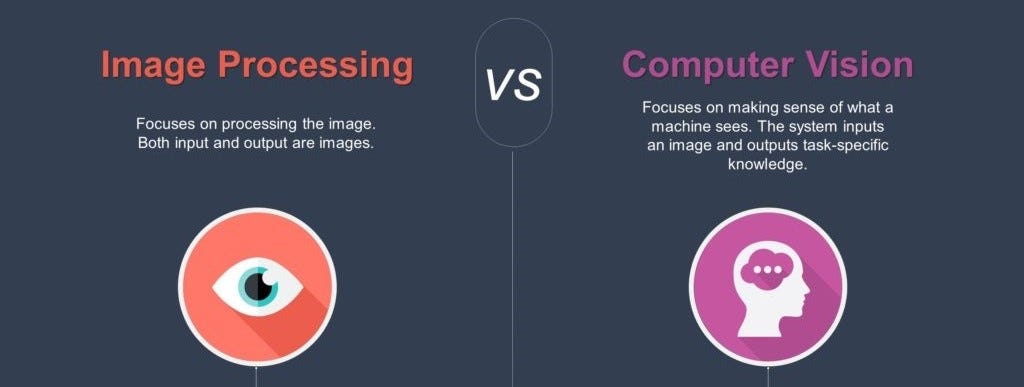
In a visual world where images hold value in many sectors, computer vision and image processing are two fields that stand out when processing visual data. Although these terms are closely related and mainly work to analyze and manipulate visual information, they also have essential distinctions. Understanding these differences between computer vision and image processing is paramount because these technologies are used widely in modern applications and can help professionals select the right technology for their needs.
For example, a security company might use image processing to refine footage quality and rely on computer vision to identify and track intruders in real-time. Similarly, image processing might be preferred in retail to elevate product photos. At the same time, computer vision could analyze shopper behavior through video feeds to improve store layouts and marketing strategies.
While they both act the same, their usage is different. This blog will explain which techniques and applications work better in computer vision and image processing to help you understand better.
Key Differences Between Computer Vision and Image Processing
Before we briefly discuss what computer vision and image processing are, how their techniques and algorithms work, and where they are applicable. Let’s examine their differences. To grasp a concept where both these techniques differ or align.
| Feature | Computer Vision | Image Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Understanding and interpreting visual information | Manipulating and enhancing images |
| Focus | Higher-level tasks (object recognition, scene understanding) | Lower-level tasks (image enhancement, filtering) |
| Techniques | Deep learning, machine learning, feature extraction | Image filtering, histogram equalization, color correction |
| Applications | Autonomous vehicles, medical imaging, facial recognition | Digital photography, image editing, video production |
| Output | Meaningful information about the visual content | Processed or enhanced images |
| Unique Feature | Semantic Understanding (extracting meaning from images) | Aesthetic manipulation (altering images for visual appeal) |
Why Compare Computer Vision and Image Processing?
The comparison is essential to help users understand computer vision and image processing for better application usage for several reasons.
- To choose the right technology for specific tasks, like redefining image quality or interpreting image content.
- To optimize the use of resources by applying the most effective technique for each unique problem.
- To stay updated with technological advancements and apply them to modern, real-world applications efficiently
Now you understand how computer vision and image processing are different. Let’s discuss what they are and how they work.
What Is Computer Vision?
Computer vision is an interdisciplinary field of artificial intelligence. It works with images but takes images as input instead of modifying or refining them. Computer vision extracts detailed insights and information. The main focus of computer vision is to program computers to gain a high-level understanding of digital images or videos, mimicking the human visual system’s ability to see and comprehend. To explain it more clearly, let’s take the example of autonomous vehicles. These cars navigate safely on roads by “watching” their surroundings. They use computer vision to detect obstacles, recognize traffic signs, identify lane markings, and predict the movements of pedestrians and other vehicles.
This happens because autonomous vehicles can process visual information in real-time, which allows them to make decisions just like a human driver, ensuring safe and efficient navigation.
Key Techniques and Algorithms
Several algorithms and techniques are used to extract in-depth information from an image or video, which helps find the particular analysis users are looking for in visual data. Some of the most common include:include:
- Object Detection: This technique identifies and locates objects within an image or video. These objects can be anything, like cars or human beings. They are best used in applications like security surveillance, where detecting intruders in real-time is crucial.
- Facial Recognition: This technique identifies and verifies individuals by analyzing facial features. It is widely used in security systems, smartphones for unlocking, and even social media for tagging people in photos.
- 3D reconstruction: This involves creating a three-dimensional model from multiple 2D images. It’s used in applications like virtual reality, where 3D models are necessary, or in medical imaging, to create 3D models of organs for better diagnosis.
Applications of Computer Vision
Computer vision usage and applications are vast and endless in the real world and in large corporations. Below are some of the applications discussed to explain how they are used.
Here are some unique and advanced ways computer vision is being used in augmented reality (AR), insights extraction, movement tracking, and identification:
1. Real-Time Customer Behavior Analysis with Augmented Reality
In retail, AR apps combined with computer vision can track customers’ behavior in real time. These apps provide insights into customer preferences by analyzing where customers look, their facial expressions, and body language. This helps retailers adjust product placements and marketing strategies to boost sales and improve customerhttps://www.folio3.ai/blog/improving-retail-customer-experience-with-alpr/ experiences.
2. Automated Quality Inspection in Manufacturing
Computer vision can automate quality checks in manufacturing. AR glasses with computer vision algorithms quickly detect and highlight product defects on an assembly line in real time. This speeds up inspections, reduces errors, and ensures that only high-quality products are produced.
3. Extracting Insights from Medical Imaging
Computer vision is transforming medical imaging analysis. For example, computer vision can examine digital slides in pathology to detect patterns or signs of diseases like cancer. This helps doctors make more accurate diagnoses, predict how a disease might progress, and create personalized treatment plans.
4. Tracking and Analyzing Movements in Sports Training
Computer vision technology can track athletes’ movements in real time and provide feedback on their techniques. It easily analyzes body posture, joint angles, and movement paths, which lets coaches give athletes detailed insights into their performance. This is especially helpful in sports like gymnastics, golf, or tennis, where small adjustments can lead to big improvements.
5. Wildlife Monitoring and Poaching Prevention
AR devices with computer vision can track animal movements and spot poaching threats in wildlife areas. Drones or cameras can detect unusual activity, such as vehicles in restricted zones or strange animal behavior, and alert rangers in real-time, helping to protect endangered species.
What Is Image Processing?
Image processing is also part of artificial intelligence and works with images, just like computer vision. It uses images as input but generates a modified image. Image processing’s primary focus is to enhance or change the image somehow—like adjusting brightness, removing noise, or sharpening edges. It involves manipulating images to redefine their quality or extract useful information. For a better understanding, let’s look at a hospital example where high-quality medical images are crucial, and no mishandling is acceptable. Image processing works best here by improving X-rays and MRI images, allowing for more accurate detection of problems.
Key Techniques and Algorithms
Many sectors require quality images, and image processing adjusts an image’s brightness to improve visibility. It also reduces noise from a scanned document or sharpens the edges to make features more transparent. Some of the techniques are discussed below.
- Filtering: This technique helps improve image quality by removing unwanted noise or smoothing out details. For example, a filter might reduce graininess in a photo or smooth out edges.
- Edge Detection: This technique identifies the boundaries of objects within an image. It’s useful for finding shapes or outlines, like highlighting the edges of a building in a photo.
- Histogram Equalization: This technique adjusts an image’s contrast. By spreading out the range of brightness levels, it makes the image clearer and more detailed, such as improving the visibility of details in a dark photo.
Applications of Image Processing
Here are some unique ways image processing is applicable.
1. Detecting Crop Diseases in Agriculture
Image processing enables farmers to detect crop problems early. The Algorithm used in image processing instantly identifies patterns or colors in plant images captured by drones or smartphones, indicating a disease or pest problem. This enables farmers to treat crops rapidly, preserving their produce while using fewer chemicals.
2. Improving Space Images in Astronomy
Telescope photos are improved through image processing. Astronomers may see distant galaxies, stars, and planets with greater clarity by decreasing noise, boosting contrast, and sharpening details. This allows people to discover more about the universe.
3. Restoring Art and Old Photos
Image processing aids in the restoration of damaged artwork and historical photographs. Digital technologies can fill in missing sections and repair damage in images by evaluating their color and texture. This helps preserve cultural history without altering the original pieces.
4. Reconstructing Faces in Forensics
Forensics uses image processing to rebuild a person’s face from skull photos. Image processing algorithms can generate a digital model of the face by researching its bone structure, which aids in the identification of unknown individuals and the resolution of crimes.
5. Checking Food Quality in the Food Industry
Image processing is used to check the quality of food. Cameras capture images of fruits, vegetables, or packaged items, and software analyzes these images for any defects or irregularities. This ensures only the best products reach customers, reducing waste and improving safety.
Use Cases of Computer Vision and Image Processing.
These use cases provide paramount information that helps to determine which industry or AI application, computer vision, or image processing works better.
1. Tesla’s Autopilot System
Tesla uses computer vision in its Autopilot feature for self-driving cars. The system relies on multiple cameras and advanced software to understand the car’s surroundings in real time. It can detect lane markings, recognize traffic signs, and identify pedestrians and other vehicles. This allows Tesla cars to drive themselves in certain conditions, keep the car in the correct lane, adjust speed, and even park automatically, making driving safer and more convenient.
2. Amazon Go Stores
Amazon Go stores use computer vision to create a checkout-free shopping experience. Cameras and sensors in the store track what customers pick up and put back on the shelves. This technology automatically adds items to a virtual cart and charges customers when they leave the store without needing a traditional checkout. This system speeds up the shopping process and reduces lines, making it more efficient and customer-friendly.
Use Cases of Image Processing
1. Adobe Photoshop for Image Editing
Adobe Photoshop is a popular software that uses image processing to edit and enhance photos. It allows users to reduce noise, adjust colors, sharpen images, and apply various filters. Both professionals and hobbyists use Photoshop to create high-quality images for digital art, printing, and web use. The software’s tools help improve image quality and create visually appealing results.
2. Google Books Project
The Google Books project uses image processing to digitize millions of library books worldwide. It scans books and uses optical character recognition (OCR) to turn images of text into searchable, editable digital text. Techniques like de-skewing and noise reduction improve the quality of scanned images, making them easier to read and search. This project helps preserve rare and old books, making them accessible online.
Intersection of Computer Vision and Image Processing
How They Complement Each Other
Image processing and computer vision often work together to accomplish complex tasks. Typically, image processing is the first step in a computer vision pipeline. It focuses on enhancing and preparing images to improve the effectiveness of computer vision algorithms. Techniques like noise reduction, contrast enhancement, and edge detection are used to clean up and refine images before they are analyzed further. These steps help ensure that the visual data is clear and of high quality, making it easier for computer vision models to accurately interpret and understand the content.
Examples of Integrated Applications
A great example of how computer vision and image processing work together is in optical character recognition (OCR) systems. OCR systems are designed to convert printed or handwritten text into digital text. Here’s how both technologies are integrated:
- Image Processing in OCR: The first step involves scanning the image to make the text more readable. Techniques like noise reduction, de-skewing, and contrast adjustment are applied to improve the clarity of the text. This processing step ensures the text stands out clearly against the background, which is essential for the next stage.
- Computer Vision in OCR: Computer vision techniques are used to recognize and interpret the characters once the image has been processed. Machine learning models, which have been trained on thousands of text samples, analyze the shapes and patterns of the characters to convert them into digital text. The accuracy of this step depends significantly on the quality of the processed image, which is enhanced through the initial image processing steps.
By combining image processing and computer vision, OCR systems can effectively convert physical documents into digital formats with high accuracy. This integration highlights how the two fields complement each other, with image processing providing a clean, high-quality input for computer vision algorithms to work with.
Tools and Libraries for Computer Vision and Image Processing
Popular Tools and Frameworks
1. OpenCV
OpenCV is a popular, open-source library for computer vision and image processing. It provides many tools for tasks like filtering images, detecting edges, and recognizing faces. OpenCV works with multiple programming languages, such as Python, C++, and Java, making it versatile for various projects.
2. TensorFlow and PyTorch
TensorFlow and PyTorch are top deep learning frameworks that support computer vision tasks. They offer pre-trained models and tools to help with image classification, object detection, and more. Both are widely used in research and industry for their powerful capabilities.
3. MATLAB
MATLAB is known for its strong image-processing features. It has built-in functions for analyzing and processing images, including filters and advanced algorithms. MATLAB is popular in research and academia for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive support.
4. Scikit-image
Scikit-image is a Python library that provides easy-to-use tools for image processing tasks like segmentation and color adjustments. It’s great for simpler projects and is built on top of other Python libraries like SciPy and NumPy.
5. Dlib
Dlib is a toolkit in C++ that’s used for tasks like face detection and object tracking. It’s known for its ease of use and powerful algorithms, making it a good choice for building computer vision applications quickly.
Choosing the Right Tool
When choosing tools and libraries, consider:
1. Project Complexity
For basic tasks, tools like OpenCV or scikit-image are sufficient. For complex tasks, such as deep learning, TensorFlow or PyTorch are better options.
2. Programming Language
Pick a tool that works with your preferred programming language. OpenCV supports multiple languages, while MATLAB is a standalone environment.
3. Performance Needs
If you need high performance, especially for deep learning, choose tools like TensorFlow or PyTorch that support GPU acceleration.
4. Support and Community
Tools with strong community support and documentation, like OpenCV, TensorFlow, and PyTorch, are easier to work with and troubleshoot.
5. Integration
Consider how well the tool integrates with your other systems or platforms. TensorFlow and PyTorch, for example, work well with cloud platforms for larger projects.
Considering these factors, you can select the best tools and libraries for your computer vision and image processing needs.
Computer Vision Vs. Image Processing: Which One Should You Use?
Now that we know the differences between computer vision and image processing, the main task is to decide which one to use. To break it more efficiently, we have put things to which one to choose for what purpose.
When to Choose Image Processing
- Preprocessing Data: Use it to enhance images before analysis, such as cleaning up scanned documents to clarify text.
- Basic Enhancements: Image processing is ideal for simple tasks like sharpening, adjusting brightness, or correcting colors. These improvements don’t require understanding the image content.
- Low Complexity Tasks: Best for projects needing visual improvements or basic changes without interpreting the content.
When to Choose Computer Vision
- Understanding Content: Use it when analyzing or interpreting an image’s content, such as detecting objects or recognizing faces. For example, a security system tracks individuals in video feeds.
- Advanced Analysis: Use it for complex tasks like autonomous driving, where the system must make decisions based on visual data, such as identifying traffic signs or detecting pedestrians.
- Automated Insights: Computer vision helps extract meaningful information from images, like spotting tumors in medical scans.
Future Trends in Computer Vision and Image Processing
These two technologies have profoundly impacted the application. Further improvements on both can undoubtedly change the interpretation of visual information.
- AI and Deep Learning: Advanced AI techniques, such as deep learning, make computer vision more powerful. These technologies help computers recognize objects and patterns with greater accuracy.
- Real-Time Processing: Faster processing power allows for real-time analysis of images and videos. This is important for applications like self-driving cars and live surveillance.
- 3D Vision and Augmented Reality (AR): New technologies are improving how we perceive and interact with digital information, like creating detailed 3D models and enhancing real-world environments with AR.
Conclusion
Computer vision and image processing are crucial technologies for analyzing and manipulating visual data. While image processing focuses on enhancing images, computer vision interprets visual content to extract meaningful information. Choosing the right technology depends on your specific needs, whether for basic enhancement or complex analysis.

Dawood is a digital marketing pro and AI/ML enthusiast. His blogs on Folio3 AI are a blend of marketing and tech brilliance. Dawood’s knack for making AI engaging for users sets his content apart, offering a unique and insightful take on the dynamic intersection of marketing and cutting-edge technology.